A toolbar can be found in each view. When you hover over the tools with the mouse, short tooltips appear to give you a quick overview of the symbols' properties.
The toolbar helps you navigate the map, create sections and synthetic boreholes, and save images.
¶ 2D-View
 Select Background Color: In each view there is a function to change the background colour. Clicking on this tool opens a colour selector. For further colours, the tab of the different colour models such as RGB or CMYK (especially suitable for printing), but also the colour spaces HSV and HSL are used.
Select Background Color: In each view there is a function to change the background colour. Clicking on this tool opens a colour selector. For further colours, the tab of the different colour models such as RGB or CMYK (especially suitable for printing), but also the colour spaces HSV and HSL are used.
 Save 2D-view as image: The image saving function can be found in all views. This function saves a photo of the model in the current settings as an image raster (jpg, png) or as SVG file.
Save 2D-view as image: The image saving function can be found in all views. This function saves a photo of the model in the current settings as an image raster (jpg, png) or as SVG file.
 Print window map: This tool allows you to print the map directly without saving it on the PC.
Print window map: This tool allows you to print the map directly without saving it on the PC.
 Zoom to full extent: This and the following two tools control the zoom into the map or model. With full extent you zoom back to the basic view.
Zoom to full extent: This and the following two tools control the zoom into the map or model. With full extent you zoom back to the basic view.
 Zoom in: With this tool, a certain area can be marked with the mouse that is to be enlarged. The tool remains activated until it is clicked again.
Zoom in: With this tool, a certain area can be marked with the mouse that is to be enlarged. The tool remains activated until it is clicked again.
 Zoom out: With click on this symbol, a gradual zoom out takes place.
Zoom out: With click on this symbol, a gradual zoom out takes place.
 Move: This can be used to move the map section / view.
Move: This can be used to move the map section / view.
 Previous View: This tool is used to switch to the previous views.
Previous View: This tool is used to switch to the previous views.
 Fit view to section extend: This tool is connected to the Cross Section View. If an area has been enlarged in Cross Section, it can be viewed in the 2D Map View. This also works the other way round. Read more about this in the Cross Section menu bar.
Fit view to section extend: This tool is connected to the Cross Section View. If an area has been enlarged in Cross Section, it can be viewed in the 2D Map View. This also works the other way round. Read more about this in the Cross Section menu bar.
 Show map in 3D View: With this tool the 2D map can be sent to the 3D model. The following information is necessary for this:
Show map in 3D View: With this tool the 2D map can be sent to the 3D model. The following information is necessary for this:
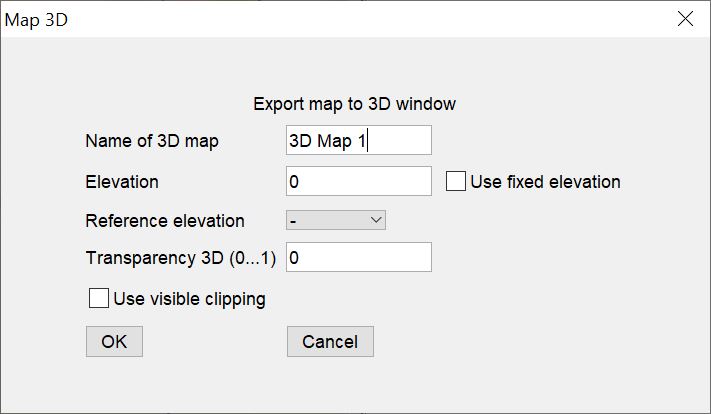
Either a concrete elevation value for the position of the map in the 3D (e.g. 50 metres above sealevel) must be specified in the text field elevation and a check mark must be set for use fixed elevation, or an elevation model (e.g. a surface grid) is used as a reference to adapt the map to it. The application is useful when the map view shows geologically relevant structures, such as the course of a significant river. Note that the dropdown\ menu for reference elevation only shows content when surface rasters or TINs are loaded. With use visible clipping the 3D image can be clipped to the map section of the current 2D map window.
 Info: The info tool is activated by clicking on the symbol. If you click and hold the mouse in the 2D window and have, for example, surfaces or shapes in the active view, you can read the information about the objects at the clicked position at the bottom of the 2D map. It can be helpful to open the info-window. There you will see a log of the clicked information. If the function is used in the 3D model, the info window opens automatically, unless you have deactivated this function in the 3D-Settings. If you are editing lines or polygons, you can use the Info tool to select individual objects by clicking precisely on the (outer) line and then carry out certain functions. Read more about it here.
Info: The info tool is activated by clicking on the symbol. If you click and hold the mouse in the 2D window and have, for example, surfaces or shapes in the active view, you can read the information about the objects at the clicked position at the bottom of the 2D map. It can be helpful to open the info-window. There you will see a log of the clicked information. If the function is used in the 3D model, the info window opens automatically, unless you have deactivated this function in the 3D-Settings. If you are editing lines or polygons, you can use the Info tool to select individual objects by clicking precisely on the (outer) line and then carry out certain functions. Read more about it here.
Note:
If you click twice in the 2D window or a profile section with the info-tool active, a window appears showing the coordinates of the click in text fields. You can use these elsewhere with copy-paste, for example if you want to set a marker at the clicked position for your documentation.
 Length measurement: This tool is only used in conjunction with the Info button.
Length measurement: This tool is only used in conjunction with the Info button.
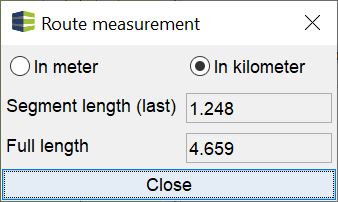
Lengths can be measured in the 2D map. After two coordinates have been set, a window appears showing the distance between the two points. A yellow connecting line shows the measured length on the map. If further coordinates are added, the distance for these points are added and the distance of the last segment is shown at the same time. To make a new measurement, the tool must be deactivated and activated again. In the Info-Window you will see a log of your length measurements.
 Synthetic log: This tool can be used to create synthetic boreholes from the calculated model or a voxel model. This means that you can read the modelled layers at this position as a vertical log. If you activate this tool with a click and then click in the map at the target position, first a dialogue opens with the corresponding coordinates. You can enter an exact coordinate in the text fields, in case you want to use this function before a planned drilling and then need the exact position. The synthetic boreholes are displayed in the Borehole-log window in the section Syn. borehole-logs. For more information read synthetic boreholes/planning boreholes.
Synthetic log: This tool can be used to create synthetic boreholes from the calculated model or a voxel model. This means that you can read the modelled layers at this position as a vertical log. If you activate this tool with a click and then click in the map at the target position, first a dialogue opens with the corresponding coordinates. You can enter an exact coordinate in the text fields, in case you want to use this function before a planned drilling and then need the exact position. The synthetic boreholes are displayed in the Borehole-log window in the section Syn. borehole-logs. For more information read synthetic boreholes/planning boreholes.
Note:
If you need synthetic logs for several positions and want to see the output less visually and more as a table, you can use the function export layers at BID positions or, for voxel models extraction at XY from voxel model. Table outputs of the synthetic logs are particularly useful if you find continuous parameter values in the voxel models.
 Create new cross section: New synthetic cross-sections or profile sections can be drawn through the calculated model with the help of the map. For more information, see create cross-section. If you need an exact profile section with integration of boreholes, you should use the function in Add objects - Create new cross section.
Create new cross section: New synthetic cross-sections or profile sections can be drawn through the calculated model with the help of the map. For more information, see create cross-section. If you need an exact profile section with integration of boreholes, you should use the function in Add objects - Create new cross section.
 Switch cross: With this, the navigation cross can be deactivated.
Switch cross: With this, the navigation cross can be deactivated.
 Update: This reloads the view.
Update: This reloads the view.
 Default settings: If the views have been hidden with the arrows or switched to 3D presentation mode, this tool can be used to restore the user interface standard.
Default settings: If the views have been hidden with the arrows or switched to 3D presentation mode, this tool can be used to restore the user interface standard.
¶ Extended toolbar for active polygon and line drawings
The extended toolbar appears as soon as you have enabled a layer, a TIN or a Geometry2D object for editing. Explanations on this can be found especially in the section set layer spread and modelling with structure maps.
¶ 3D-View
In the section, the symbols that are not in the 2D-View toolbar are explained, or symbols which have slightly different functions. So look here for a full explanation.
 Save 3D-view as image: This function saves an image from the current view as an image raster (jpg, png). The size of the output image depends on the screen size of your current 3D view. When you press this button, a small dialog will appear asking you to enter a "magnification factor " (number of pixels * factor). This will make the image either larger or smaller by this factor.
Save 3D-view as image: This function saves an image from the current view as an image raster (jpg, png). The size of the output image depends on the screen size of your current 3D view. When you press this button, a small dialog will appear asking you to enter a "magnification factor " (number of pixels * factor). This will make the image either larger or smaller by this factor.
 Plan view: This tool displays the model from above (bird perspective).
Plan view: This tool displays the model from above (bird perspective).
 Side View: This perspective shows the model in the exact horizontal position (no tilt).
Side View: This perspective shows the model in the exact horizontal position (no tilt).
 Select standard view direction: This tool can be used to determine the direction from which the 3D graphic is to be viewed. E stands for east, N for north, NW for northwest, etc., + T for from above, B for from below.
Select standard view direction: This tool can be used to determine the direction from which the 3D graphic is to be viewed. E stands for east, N for north, NW for northwest, etc., + T for from above, B for from below.
 Counter-clockwise rotation or play video: The model can be rotated counterclockwise with this tool. With another click on this tool
Counter-clockwise rotation or play video: The model can be rotated counterclockwise with this tool. With another click on this tool  the animation is stopped.
the animation is stopped.
 Clockwise rotation or play video reverse: The model can be rotated clockwise with this tool. With another click on this tool
Clockwise rotation or play video reverse: The model can be rotated clockwise with this tool. With another click on this tool  the animation is stopped.
the animation is stopped.
 Fix anchor & rotation point: This tool can be used to fix a point in the model. The model rotates around this point.
Fix anchor & rotation point: This tool can be used to fix a point in the model. The model rotates around this point.
 Vertical exaggeration: This allows the vertical scale of the model to be rescaled. The vertical features that may be too small to be identified in relation to the horizontal scale are highlighted.
Vertical exaggeration: This allows the vertical scale of the model to be rescaled. The vertical features that may be too small to be identified in relation to the horizontal scale are highlighted.
 Switch on/off anaglyphs: With this tool, the 3D model can be viewed with red-green 3D glasses. This is the anaglyph technique.
Switch on/off anaglyphs: With this tool, the 3D model can be viewed with red-green 3D glasses. This is the anaglyph technique.
Note: If you have a 3D screen, you can take a closer look at the settings of the 3D-view. There you will find settings that show your model on a 3D screen with depth.
 Full screen on/off: This tool hides all menus, window frames and toolbars. When the full screen view is on, press the ESC key to exit full screen mode.
Full screen on/off: This tool hides all menus, window frames and toolbars. When the full screen view is on, press the ESC key to exit full screen mode.
Note:
The toolbar of the 3D window can be detached from the window frame and moved. To do this, click on it in the empty area between the options, hold the mouse down and drag it away. When the 3D toolbar has been closed, it is automatically placed in its place in the 3D window.
 Update: This reloads the view. It is helpful if an object temporarily contains no data values and thus the vertical extension of the 3D view no longer makes sense.
Update: This reloads the view. It is helpful if an object temporarily contains no data values and thus the vertical extension of the 3D view no longer makes sense.
¶ 2D-Cross-Section View
In the section, the symbols that are not in the 2D-View toolbar are explained. So look here for a full explanation. The drawing symbols that are greyed out in the image above are covered in the article construct profile sections.
 Move notice: Note pins can be moved in the profile section. How to generate note pins is explained here.
Move notice: Note pins can be moved in the profile section. How to generate note pins is explained here.
 Fit view to section extend: This tool is linked to the 2D Map View. In the area of a cross section, the 2D map (or vice versa the 2D Cross Section View) adjusts. In this way, the same area can be seen in both views.
Fit view to section extend: This tool is linked to the 2D Map View. In the area of a cross section, the 2D map (or vice versa the 2D Cross Section View) adjusts. In this way, the same area can be seen in both views.
 Draw line: This tool makes it possible to draw lower layer edges. After choosing the Layer from the drop-down menu (see below), a line can be drawn by setting support points. The buffer zone of the "snapping" line is increased around the cursor by pressing Strg and +. This increases the line's distance from the layer border in the boreprofile. With Strg & -, the zone can be reduced. The final point on a line must be set with a double click to complete it.
Draw line: This tool makes it possible to draw lower layer edges. After choosing the Layer from the drop-down menu (see below), a line can be drawn by setting support points. The buffer zone of the "snapping" line is increased around the cursor by pressing Strg and +. This increases the line's distance from the layer border in the boreprofile. With Strg & -, the zone can be reduced. The final point on a line must be set with a double click to complete it.
 Edit line: It is possible to adjust and move the support points of the previously drawn lower layer edges/lines using this tool. Bases can be deleted by double clicking on them.
Edit line: It is possible to adjust and move the support points of the previously drawn lower layer edges/lines using this tool. Bases can be deleted by double clicking on them.
Mit diesem Werkzeug können die Stützpunkte (Knotenpunkte) der zuvor gezeichneten Schichtunterkanten/Linien verschoben und angepasst werden. Mit einem Doppelklick auf Stützpunkte können diese gelöscht werden. With a click between set support points you add a support point.
Note: The support points represent the input data that flow into the area calculation, i.e. the triangulation of the lower and upper edge of the layer. Their positioning is therefore as important as the support points of the layer boundary. For more information read the sections: construct profile sections, define layer distribution and modelling with structure maps.
 Split line: The outlined lower layer edges/lines can be cut into pieces with this tool. You can create a "path" by clicking on several different points. The final point needs to be double-clicked to complete this flow and begin the cutting process. They are divided at each location where a lower edge crosses this path.
Split line: The outlined lower layer edges/lines can be cut into pieces with this tool. You can create a "path" by clicking on several different points. The final point needs to be double-clicked to complete this flow and begin the cutting process. They are divided at each location where a lower edge crosses this path.
 Add borehole to section: With this, drill points can be added to the cross-section view (profile section) after they have been selected in the 2D map with the info tool. For more information, read Construct Profile Sections.
Add borehole to section: With this, drill points can be added to the cross-section view (profile section) after they have been selected in the 2D map with the info tool. For more information, read Construct Profile Sections.
 Add point to section: This tool facilitates the expansion of 2D map cross sections into cross section views. By using the info tools in the 2D map and the add point to section option in the menu bar of the cross-section view, more points can be added to sections that have been created by the user or that are already there. The line is hung right to the existing or right to the sectional view in existing sections. For more information, read profile cuts.
Add point to section: This tool facilitates the expansion of 2D map cross sections into cross section views. By using the info tools in the 2D map and the add point to section option in the menu bar of the cross-section view, more points can be added to sections that have been created by the user or that are already there. The line is hung right to the existing or right to the sectional view in existing sections. For more information, read profile cuts.
 Delete last drill log/ coordinate: The previously chosen coordinate in the 2D map can be changed, and the relevant section of the cut is eliminated.
Delete last drill log/ coordinate: The previously chosen coordinate in the 2D map can be changed, and the relevant section of the cut is eliminated.
 Update: The polygons to the sections are not automatically redrawn after changes. In very large areas where long, complex sections may exist, it has proven disadvantageous to force a dynamic update of the view. Therefore, you should click update so that your latest changes are actually visible and the layer polygons are redrawn.
Update: The polygons to the sections are not automatically redrawn after changes. In very large areas where long, complex sections may exist, it has proven disadvantageous to force a dynamic update of the view. Therefore, you should click update so that your latest changes are actually visible and the layer polygons are redrawn.
 Selection of Layer: Here, the draw line function's drawing-ready layer is selected.
Selection of Layer: Here, the draw line function's drawing-ready layer is selected.
 Addition label of borehole: This can be used to select additional titles for the drill holes. They appear as text above the drill point.
Addition label of borehole: This can be used to select additional titles for the drill holes. They appear as text above the drill point.
 Limited refresh off: With this tool, sections that are very large and contain a lot of data can be drawn in a limited way. Data that is character-intensive is not displayed.
Limited refresh off: With this tool, sections that are very large and contain a lot of data can be drawn in a limited way. Data that is character-intensive is not displayed.